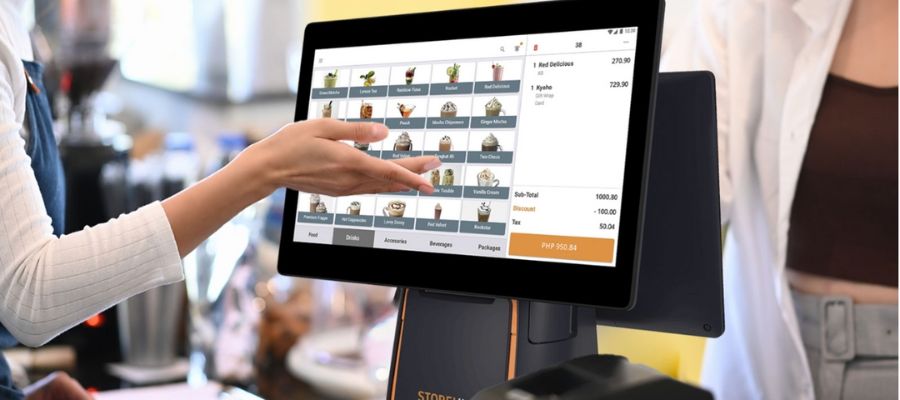
POS System Hardware And Software: What You Need To Know
It is also important for the business organizations that are involved in the sale of goods and services to have POS systems well functioning. From a small retail shop to a busy restaurant, a POS helps manage processes, improve clients’ experience and generate essential data. To keep up with the technologically connected world, this article will focus on POS system meaning, POS system examples, POS system hardware and POS software functions and uses, and how to properly implement one.
POS System Full Form
POS means Point of Sale. This means the location of buyer-seller transactions in retailing. It encompasses the devices and applications that support the transaction: from scanning the goods and collecting the payment to ordering the stock and creating the reports.
POS System Hardware
1. POS Terminal
The POS terminal is the primary interface that enables the completion of the transactions since it is the main processing equipment. Nowadays, POS terminals may be personal computers, tablets or special POS equipment.
2. Cash Drawer
A check cash drawer is used to keep money transactions as secure as possible. This links to the point of sale terminal and opens every time a cash transaction is processed in the shop.
3. Receipt Printer
Customer receipts are produced on receipt printers as a receipt of the purchase by the client. Thermal printers are widely used because they are fast and do not require any ribbons.
4. Barcode Scanner
There are several point-of-sale equipment; including barcode scanners which aid in the scanning of products’ barcodes and lessen the likelihood of having key-in mistakes as well as offer a faster checkout.
5. Card Reader
The point-of-sale terminal that is used in accepting credit and debit cards is also known as a card reader. New card readers allow chips, magnetic strips, as well as NFC payments.
6. Customer Display
A customer display presents the full details of the performed transaction of the customer to avoid any instances of malpractice or the customer not getting a clear understanding of a product or service he or she has bought.
7. Network Infrastructure
POS links the various other components together; therefore, a reliable network infrastructure is vital to establishing connectivity between the different POS components.
POS System Software
1. Sales Processing
The primary role of POS software is to manage the sales between the merchant and the customers. This encompasses s for example, the operations of bar code scanning, total arriving at and determination, application of discounts as well as payment processing.
2. Inventory Management
POS has tools that can track goods’ stock and suggest when the stocks are low and at what time to order for stock. It is useful in ensuring that adequate stock is procured and the expiration of products is avoided.
3. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM components enable the customer’s details to be kept, a record of their purchases made to be retained and loyalty programs to be developed. It assists in the customization of the marketing strategy and improving the fortunes of consumers.
4. Reporting and Analytics
POS software comes with the ability to produce countless reports inclusive of the overall sales, inventory, employees, and customers’ activities. It is useful in formulating business decisions by providing such information.
5. Employee Management
Sometimes time is recorded or the shifts are planned to control the workers to track the performance of the workers.
6. Integration Capabilities
The major advantage of contemporary POS systems is that they are compatible with other business applications such as accounting software, e-commerce platforms, and marketing tools so that all the operations of the company are interconnected.
Examples of POS Software
-
Square POS: popular for its ease of use and strong capabilities, suitable for companies that are small to medium in size.
-
Shopify POS: Very well integrated with Shopify’s e-commerce solution making it perfect for companies that are in the retail industry.
-
Toast POS: Designed for the restaurant business and includes such tools as table control, order management, and uniting with the kitchen display.
How to utilise Point of Sale System
1. Setting Up
-
Install Hardware: Screw all the hardware peripherals, from the terminal, the cash drawer, the printer and the barcode scanner.
-
Install Software: Install the POS software on the terminal and set it up in such a manner that is suitable for your enterprise.
-
Connect to Network: This is especially an important factor because all the components should be on the same network for them to communicate.
2. Training Staff
-
Basic Operations: Educate the staff in the simplest functions of the business such as item scanning, methods of payment, and generating receipts.
-
Advanced Features: Explain to the staff all the options such as inventory, CRM, and more, which are included in QuickBooks.
3. Processing Transactions
-
Scan Items: You must use the handgun-shaped barcode scanner and handgun-shaped ‘keyboard’ to scan in barcodes/enter them in manually if they do not have barcodes.
-
Apply Discounts: We need to apply discount coupons or promotion deals if available.
-
Process Payment: Select the type of payment (cash, credit card, mobile) and go ahead making the payment.
-
Print Receipt: Inform the customer and offer them a printed or electronic receipt.
4. Managing Inventory
-
Track Stock: They should update the inventory management frequently and create notifications for running low on stock.
-
Reorder Products: Apart, there is synchronization of optometric devices and consumables with the purchasing system to avoid running out of stock.
5. Generating Reports
-
Sales Reports: Create daily, weekly, and or monthly sales reports to help monitor the progress.
-
Inventory Reports: Watch over the quantities of the products, and find out which ones are not selling as expected.
-
Customer Reports: Crunch customer statistics to determine how best to market products to the demographic.
GUIDELINES ON CHOOSING POINT OF SALE SYSTEMS FOR SMALL BUSINESS
1. Affordability
Small business's funding is most of the time-limited and therefore, affordable POS systems are ideal. Some of the solutions are web-based and include Square, and Shopify POS among others and they are cheap with basic functionalities.
2. Scalability
Scalability helps to prevent launches from becoming splendid failures as well as gives growing small businesses the means to expand without having to redesign the entire POS system that they are using. Select a system that is easily upgradable to add on new functionalities or when expanding to other outlets.
3. Ease of Use
A readily customizable design with user interface elements is crucial for small businesses that do not have a team of programmers. Ease and lower complexity of the setting also entails less time spent in training and fewer operational mistakes.
See Below Some Of The POS Systems For Small Business
-
Square POS: Cheap and easy to use, recommended for many different types of businessmen and businesswomen.
-
Shopify POS: Perfect for businesses that have an online store.
-
Vend POS: Web-based, which has very good functionality for managing inventory, ideal for use in retail stores.
POS Machine
A POS machine, often referred to as a POS terminal, is the device used to process transactions at the point of sale. It includes the hardware and software needed to complete sales, manage inventory, and generate reports.
Features of a POS Machine
-
Touchscreen Interface: Modern POS machines often feature touchscreen interfaces for easy navigation and operation.
-
Integrated Card Reader: Allows for seamless processing of credit and debit card payments.
-
Connectivity: Connects to peripheral devices like barcode scanners, receipt printers, and cash drawers.
-
Portability: Some POS machines are portable, making them ideal for businesses that operate in multiple locations or on the go.
POS System for Retail
Retail POS systems are designed to handle the specific needs of retail businesses, from small boutiques to large department stores. Key features include inventory management, customer tracking, and sales reporting.
Retail POS Features
-
Inventory Management: Tracks stock levels, generates alerts for low stock, and automates reordering.
-
Customer Management: Stores customer data and purchase history, enabling personalized marketing.
-
Sales Reporting: Provides detailed sales reports to analyze performance and identify trends.
-
Multi-Location Support: Manages inventory and sales data across multiple store locations.
Examples of Retail POS Systems
-
Lightspeed Retail: Offers comprehensive inventory management and detailed reporting features.
-
Shopify POS: Integrates with Shopify’s e-commerce platform, ideal for businesses with both online and offline stores.
-
Vend POS: Provides robust inventory and customer management features, suitable for various retail environments.
What is a POS Person?
A POS person refers to an employee who operates the POS system. This role is crucial in ensuring smooth transactions and excellent customer service.
Responsibilities of a POS Person
-
Operating the POS System: Scanning items, processing payments, and issuing receipts.
-
Customer Service: Assisting customers with inquiries, returns, and exchanges.
-
Inventory Management: Updating stock levels and managing product displays.
-
Reporting: Generating sales reports and providing management insights.
Conclusion
Understanding the essential features of POS system hardware and software is crucial for any business looking to streamline operations and improve customer service. From affordable options for small businesses to comprehensive solutions for retail and restaurants, modern POS systems offer a wide range of functionalities. By choosing the right POS system, training staff effectively, and leveraging advanced features, businesses can enhance their efficiency, make informed decisions, and provide an exceptional customer experience. For a more detailed guide, including illustrations and further reading, you can download our comprehensive PDF on "POS System Hardware and Software: What You Need to Know.”


